Testosterone cypionate and testosterone enanthate represent two of the different types of testosterone accessible for therapeutic use. Both are used in TRT to help people who have low testosterone levels get back to normal, but they do have some differences that could make one a better fit for you.
A study found that taking 250 mg of testosterone enanthate by a shot in the muscle every three weeks worked well to bring testosterone levels back to normal. On the other hand, testosterone cypionate, when given the same way, keeps testosterone levels steady in a different way, with levels going up and down more over time.
It’s important to know about these differences to make the best choice for your health. This post is here to help clear up the differences, making it easier for you to decide which option might work best for your situation.
Schedule Your Free TRT Consultation Here
Understanding Testosterone Cypionate and Testosterone Enanthate
Testosterone Cypionate and Enanthate are both long-acting forms of testosterone. They are injected into the muscle, where they are stored and gradually released over time.
The method ensures a steady flow of testosterone into your bloodstream, helping to mimic the natural rhythm of testosterone production in the body. The goal with either form is to alleviate the symptoms of low testosterone, such as fatigue, loss of muscle mass, and decreased libido, improving your overall quality of life.
Both forms are highly effective in managing low testosterone, but they differ slightly in their chemical structure and how often they need to be administered. Understanding these differences is key to choosing the treatment that fits best with your lifestyle and health goals.
Key Features of Test C and Test E
Exploring the key features of Testosterone Cypionate and Testosterone Enanthate reveals their unique properties and how they influence TRT outcomes. Let’s look into their chemical structure and uses to better understand which option might suit your needs.
Chemical Structure
The primary difference between Testosterone Cypionate (Test C) and Testosterone Enanthate (Test E) lies in their chemical structure, specifically the ester attached to the testosterone molecule.
The ester affects the rate at which the testosterone is released into your bloodstream. Test C has a slightly longer carbon chain, meaning it has a longer half-life and can remain in your body a bit longer than Test E. This subtle difference influences how frequently you need injections, with Test C typically requiring slightly less frequent dosing.
Uses
Both Test C and Test E are used to treat the same conditions, primarily hypogonadism or low testosterone levels in men. They are effective in restoring testosterone levels to a normal range, which can improve symptoms such as low energy levels, reduced strength, and sexual dysfunction. The choice between the two often comes down to personal preference, availability, and how your body responds to the treatment.
Read More: Does TRT Make You Infertile?
Benefits of Cypionate and Enanthate
Even though both forms are designed to improve testosterone levels they offer different advantages for individuals experiencing low testosterone. Here’s how these treatments can positively impact your health and well-being:
Improved Muscle Mass and Strength
Both Cypionate and Enanthate are effective in increasing muscle mass and strength. This is particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing muscle wasting or weakness due to low testosterone levels. By enhancing protein synthesis and promoting muscle growth, these treatments can help you regain physical strength and endurance.
Enhanced Mood and Cognitive Function
Low testosterone levels are often linked to mood swings, irritability, and cognitive challenges. Treatment with either Cypionate or Enanthate can improve these symptoms, leading to a better overall mood and enhanced cognitive function. Many patients report feeling more mentally sharp and emotionally stable after starting TRT.
Increased Libido and Sexual Function
One of the most common reasons individuals seek TRT is for the improvement of sexual health. Both Testosterone Cypionate and Enanthate can significantly increase libido and improve erectile function, addressing issues related to low testosterone such as erectile dysfunction and reduced sexual desire.
Improved Bone Density
Testosterone plays a crucial role in bone mineral density. Treatment with Cypionate or Enanthate can help prevent osteoporosis and bone fractures by increasing bone density. This is particularly important as one age and the risk for bone-related health issues increases.
Better Fat Distribution
TRT with either Cypionate or Enanthate can lead to better body composition by reducing fat mass and increasing lean body mass. This not only contributes to a more desirable physical appearance but also to better health outcomes by reducing the risk of obesity-related diseases.
Differences of Testosterone Cypionate and Testosterone Enanthate
While Testosterone Cypionate and Testosterone Enanthate share many similarities in their application for testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), understanding their differences can help you make an informed decision tailored to your needs. Here’s a detailed comparison based on price, dosage, side effects, and cycles.
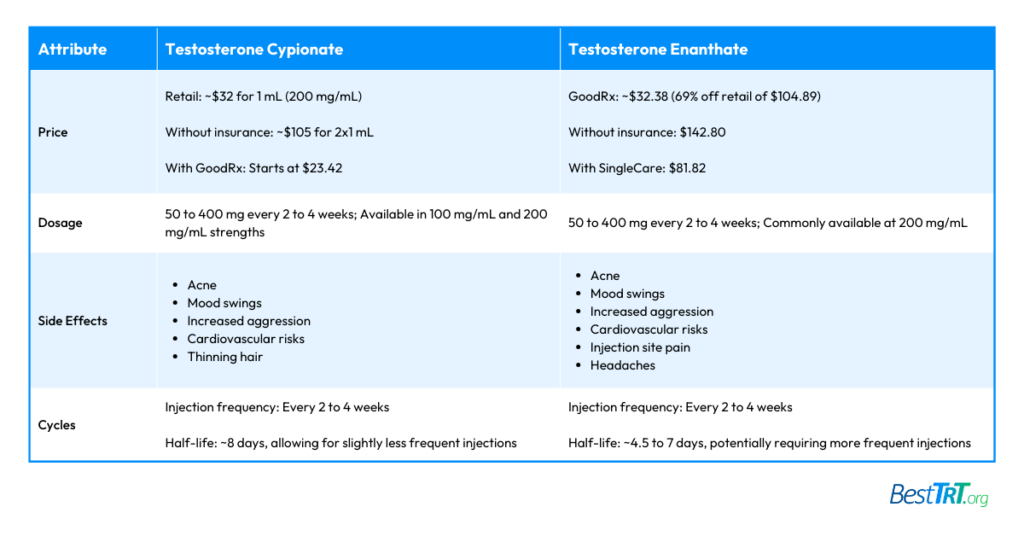
Price
- Testosterone Cypionate: The retail cost for the intramuscular solution (200 mg/mL) is about $32 for 1 milliliter, varying by pharmacy. Without insurance, the cost for 2 vials of 1 mL at 200 mg each is approximately $105. However, prices can start at $23.42 with a GoodRx coupon.
- Testosterone Enanthate: The lowest price on GoodRx for the most common version is around $32.38, which is 69% off the average retail price of $104.89. Without insurance, the cost is $142.80, but with a SingleCare coupon, it can be reduced to $81.82 at participating pharmacies.
Dosage
Both Testosterone Cypionate and Enanthate are typically administered at a dosage range of 50 to 400 mg intramuscularly every 2 to 4 weeks. However, they differ slightly in available strengths:
- Testosterone Cypionate is available in strengths of 100 mg/mL and 200 mg/mL.
- Testosterone Enanthate is commonly available at 200 mg/mL.
Side Effects
The side effects for both forms of testosterone are similar, including acne, mood swings, and other androgenic effects like increased aggression and cardiovascular risks. However, there are slight variations:
- Testosterone Cypionate may lead to thinning hair among its common side effects.
- Testosterone Enanthate side effects include injection site pain and headaches, alongside mood changes.
Cycles
The injection frequency for both Testosterone Cypionate and Enanthate is typically every 2 to 4 weeks, adjusted based on individual response. Their half-lives, which influence how often injections are needed, differ:
- Testosterone Cypionate has a half-life of approximately 8 days, allowing for slightly less frequent injections.
- Testosterone Enanthate has a shorter half-life of about 4.5 to 7 days, potentially requiring more frequent injections to maintain stable testosterone levels.
The Verdict: Which Is Better?
Deciding whether Testosterone Cypionate or Enanthate is “better” depends on individual needs, preferences, and how your body responds to treatment. Both forms are effective in treating low testosterone, with the choice often coming down to factors like dosing convenience, cost, and personal tolerance to side effects.
It’s important to have a detailed discussion with your healthcare provider, considering all aspects of your health and lifestyle. They can help you weigh the benefits and differences, guiding you toward the choice that will best support your health goals.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of TRT comes down to personalization, monitoring, and adjustment based on your body’s response.
FAQs
Is there a one-size-fits-all TRT protocol?
No, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all TRT protocol. Treatment is highly individualized based on your unique health profile, testosterone levels, symptoms, and how you respond to therapy. Your healthcare provider will tailor your TRT plan to best meet your needs, adjusting dosage and frequency as necessary.
Do Testosterone Medications Reduce Fertility?
Yes, testosterone medications can reduce fertility by decreasing sperm production, a concern often raised with TRT. If fertility is a goal, discuss alternative treatments or strategies with your healthcare provider to mitigate this effect.
Can I switch from cypionate to enanthate?
Yes, switching between testosterone cypionate and enanthate is possible and may be recommended based on your treatment response, preferences, or availability of the medications. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your TRT regimen to ensure a smooth transition and maintain stable testosterone levels.
Ready to Optimize Your Health?
Deciding between testosterone cypionate and enanthate hinges on personal health needs and doctor’s advice, as both offer effective hormone replacement solutions.
Best TRT, an innovative online TRT provider, stands out by providing personalized TRT plans, aligning with your unique health profile and goals. With expert consultations and continuous support, Best TRT guides you through the process, ensuring informed decisions about your treatment.
Schedule Your Free TRT Consultation Here and let our experts guide you through the options, ensuring your treatment aligns with your health goals and lifestyle.